Physics, CO2 storage capabilities, performance, field management, and usability form the core pillars of the Intersect™ high-resolution reservoir simulator. The release of the Intersect 2024.3 package delivers key features and updates reflecting these key focus areas.
Key release highlight
Accelerate reservoir models runtime with Intersect 2024.3: Windows GPU now available!
Intersect 2024.3 now runs on GPU architectures on the Windows operating system, enabling reservoir models to leverage its accelerated performance capabilities. It is particularly useful for customers with limited investments in computing infrastructure. This functionality supports NVIDIA GPUs that use Turing or Ampere architectures.
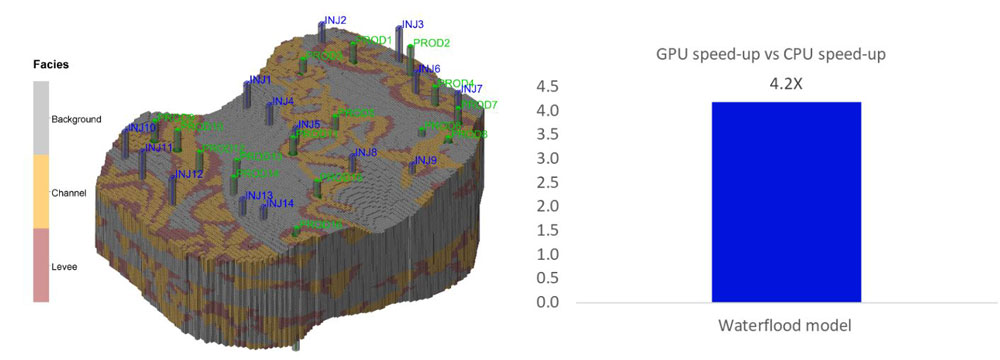
Waterflood model with 3.2 million grid cells was run using the new Windows-based GPU on Intersect 2024.3, achieving 4.2x speedup compared to running same model on CPU (GPU: NVIDIA RTX A5000 24GB vs CPU: 2x Intel Xeon Gold 6240R 24-cores)
Key enhancements
Performance
- To improve the performance of thermal CCS models, a new method for computing scale factors when the primary variables hit their upper and lower bounds has been added. Global scale factors are no longer affected by limiting the primary variable within their range, enabling the simulation to converge faster.
- A set of recommended numerical settings for isothermal and thermal CO2 storage simulations has been added to the technical documentation. Using the latest developments, these aim to provide a good balance between performance and accuracy.
Physics and CO2 Storage
- The range of analytical aquifer models has been extended to include constant pressure gas and water aquifers, including brine. These are supported in black oil and compositional simulations and can be used to efficiently model large bodies of gas or water under the assumption of constant pressure (such as a section open to atmospheric conditions).
- Relative permeability hysteresis effects following the Killough model are now available in oil-wet rocks. This feature complements the default "water-wet" hysteresis model assumptions, where these different types of wettability can be combined in a single reservoir. The "oil-wet" Killough hysteresis replicates the corresponding algorithm in Eclipse™ industry-reference reservoir simulator, and the migration of the relevant keywords to the Intersect simulator is now possible.
- Improved steam tables have been set as the new defaults for thermal models with component solubility in water (CSIW) and isothermal models with CSIW that use the Ezrokhi model. Properties such as density and viscosity of the water phase now consider pure water properties using INTERSECT_TABULAR steam tables.
Usability
- Intersect 2024.3 can handle simulations that exceed the year 9999, with the capability to run with simulation time up to approximately 252 million years. This can be utilized in geothermal and CO2 storage workflows where geological time scale predictions may be necessary.
- A new table has been added to the PRT file while parsing RESQML files (.epc) that contains information about the properties found in the file, their associated grid, and attachment kind (cells, edges, and so on).
