The new release brings improvements in physics, CO2 storage capabilities, performance, and more.
Key release highlight
Low temperature modelling of CO2 depleted reservoirs now available!.
You can now simulate processes where the temperature falls below the freezing point of water, for example, cooling due to the Joule-Thomson effect when supercritical CO2 is injected into depleted gas reservoirs. This functionality warns the user when potential hydrate formation conditions are reached, without rigorous modeling of the ice or gas hydrates.
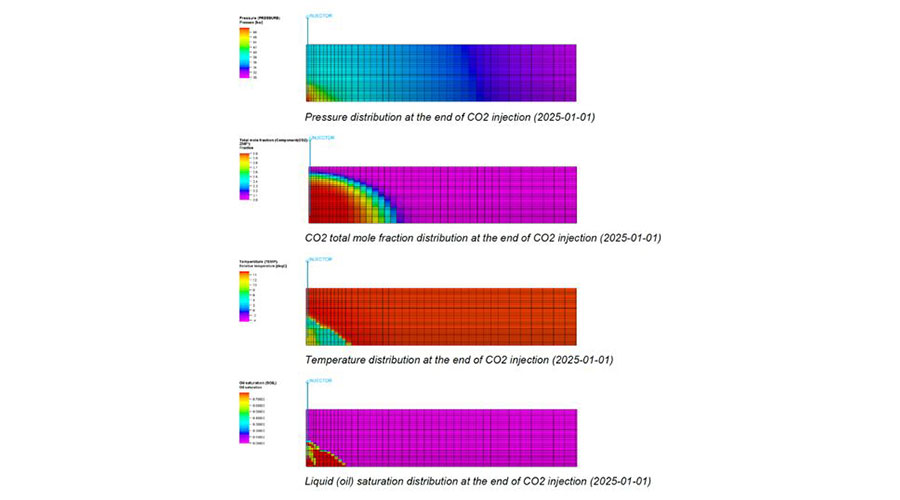
Simulation results of low temperature CO2 injection in a depleted reservoir
Improved automatic tuning feature for carbon capture, utilization and sequestration (CCUS) cases!
The automatic tuning feature has been extended to improve the accuracy and performance of CCUS cases, up to 3.6 times faster in tested models. It is also applicable to other storage types (such as hydrogen) and for chemical enhanced oil recovery (EOR) injection. This feature is activated through the TuningCO2Store field under the NumericalTuning node.

Enhanced multiscale sequential fully implicit (SFI) solver for better performance in embedded discrete fracture model (EDFM) cases!
To improve performance, new functionalities have been applied to the transport solver for EDFM cases run in Multiscale SFI. In certain cases, this new functionality was observed to run up to 2.4 times faster in tested models, compared to previous versions, without changes to results.

Key enhancements
Physics and CO2 Storage
- Relative permeability hysteresis and low salinity flooding models can now be combined, and the Killough and Carlson hysteresis models are both supported. Drainage and imbibition functions in both high and low salinity conditions are required for each corresponding rock region
- Five new workflow examples are introduced to illustrate different aspects of CO2 storage modeling, for both saline aquifers and depleted reservoirs, including all recent functionality introduced in the simulator
Field management
- You can now modify the network mapping of the NetworkBalanceAction node without the need to redefine the entire node map. The new ModifyNetworkNodeAction node enables dynamic changes to network mapping over time in network-coupled simulations. This simplifies shifting wells between surface networks, e.g. from a high-pressure to a low-pressure system
Usability
- To report the amount of a component in mass that is present in the reservoir, the LIQUID_COMPONENT_MASS and TOTAL_COMPONENT_MASS summary results are now available to request at field, grid cell, and region levels. These can also be requested as a dynamic 3D property under Recurrent3DReport. These reports are useful in applications like new energies where quantifying CO2 and H2 storage is important
- The new MaxNNCTrans field in the CellActivity node can limit the maximum transmissibility between non-neighbour cells. You can combine this feature with the MinNNCTrans field to establish physical limits for transmissibility values. This can reduce the complexity of the solution
