Release highlights
Be more agile, solve complex processes, and progress on your journey to sustainability and profitability
Symmetry™ process simulation software helps users model process workflows in a single collaborative environment, while integrating pipelines, pipe networks, facilities models, and flare systems to enable consistent thermodynamics and fluid characterization across the whole system. With Symmetry software, users can switch between steady-state and dynamic modeling, optimize processes in upstream, midstream, downstream, and new energy sectors, and maximize the total value of the asset.
Predict CO2 capture performance of any solvent
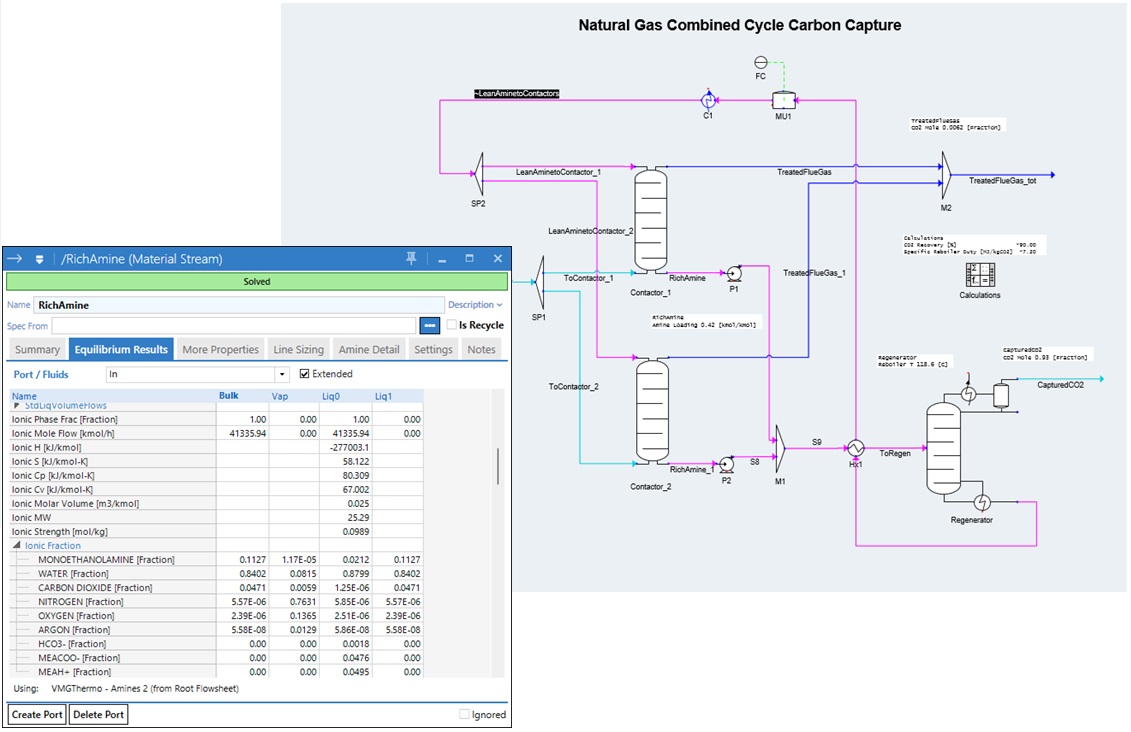
Amines 2 is a new and improved thermodynamic model tailored for CO2 capture and natural gas sweetening, with equilibrium prediction for any solvent makeup, whether chemical (reactive amines), physical (polar), or a combination. Beyond extended validation ranges for incorporated solvents, improvements include enhanced accuracy of phase equilibrium, interaction parameters of solvents and acid gases, and heat of reaction prediction. Activity coefficient and heat of absorption parameters are also exposed for user tuning.
For R&D into novelty solvent formulations and additional tuning to experimental data, Amines 2 offers the flexibility to incorporate user-defined amines and custom reactions beyond those available in the Symmetry software database. Contact us for more information on these advanced features.
Analyze green hydrogen production over time
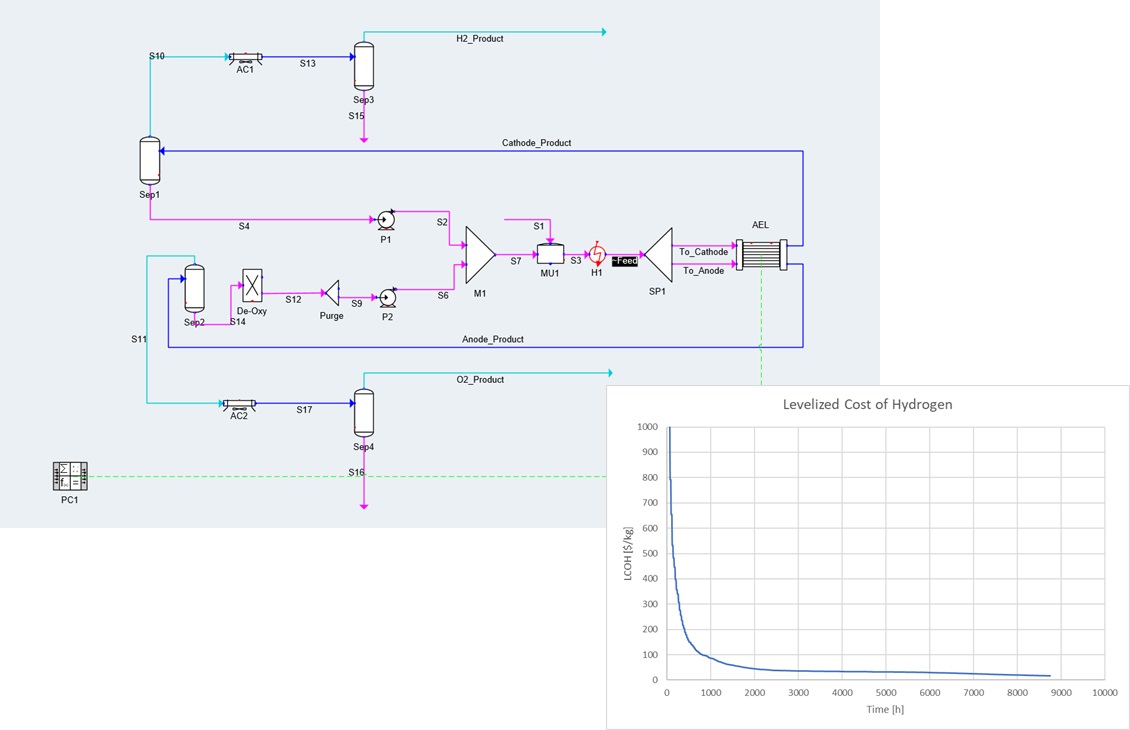
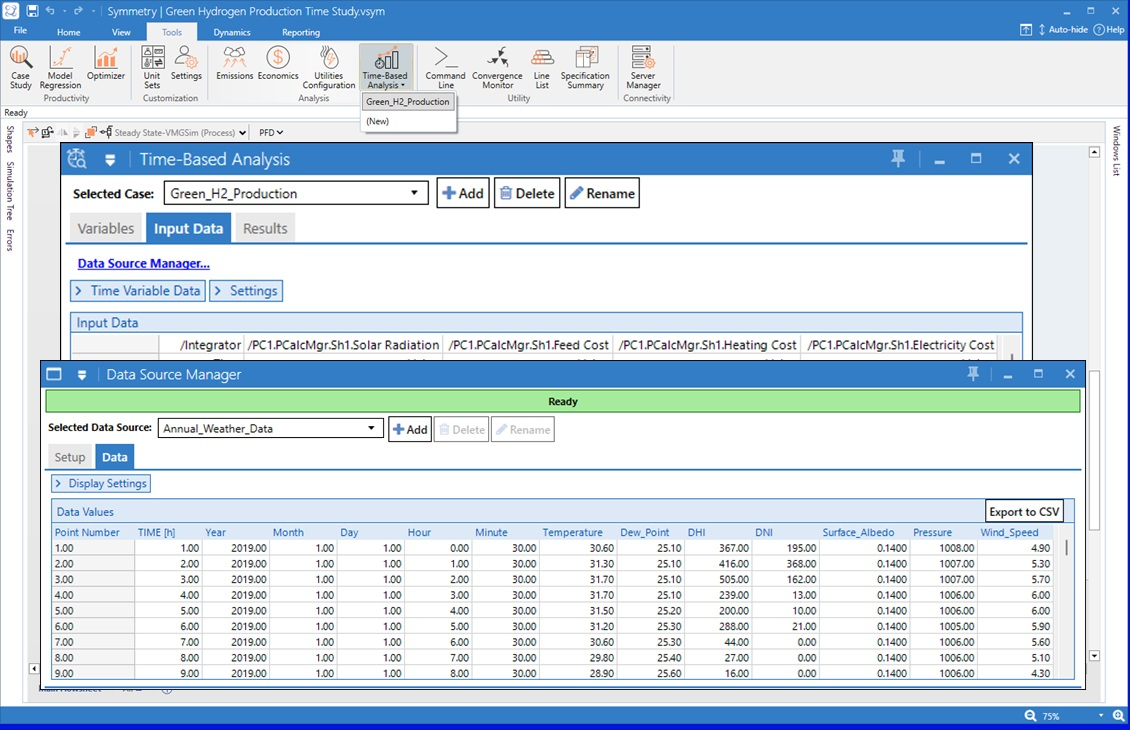
A newly added “Time-based analysis” tool enables modeling of processes for long-term planning and evaluations. Such steady-state time-based studies are especially relevant in green hydrogen production, where factors like the power available to an electrolyzer, equipment decay, costs, and pricing fluctuate meaningfully over time. A technoeconomic evaluation or operational planning study can be conducted by first specifying how key input parameters change over time, and then tracking pertinent calculated values through a batch run of the simulation.

Large input data sets (for example, a weather forecast) can be imported through a csv file and managed in a data source manager for reuse in multiple studies.
Time-tracked results are easily exportable as a csv file for further analysis and custom reporting. These productivity tools can thus ease decision making on the economic feasibility and optimal operation of a green hydrogen project.
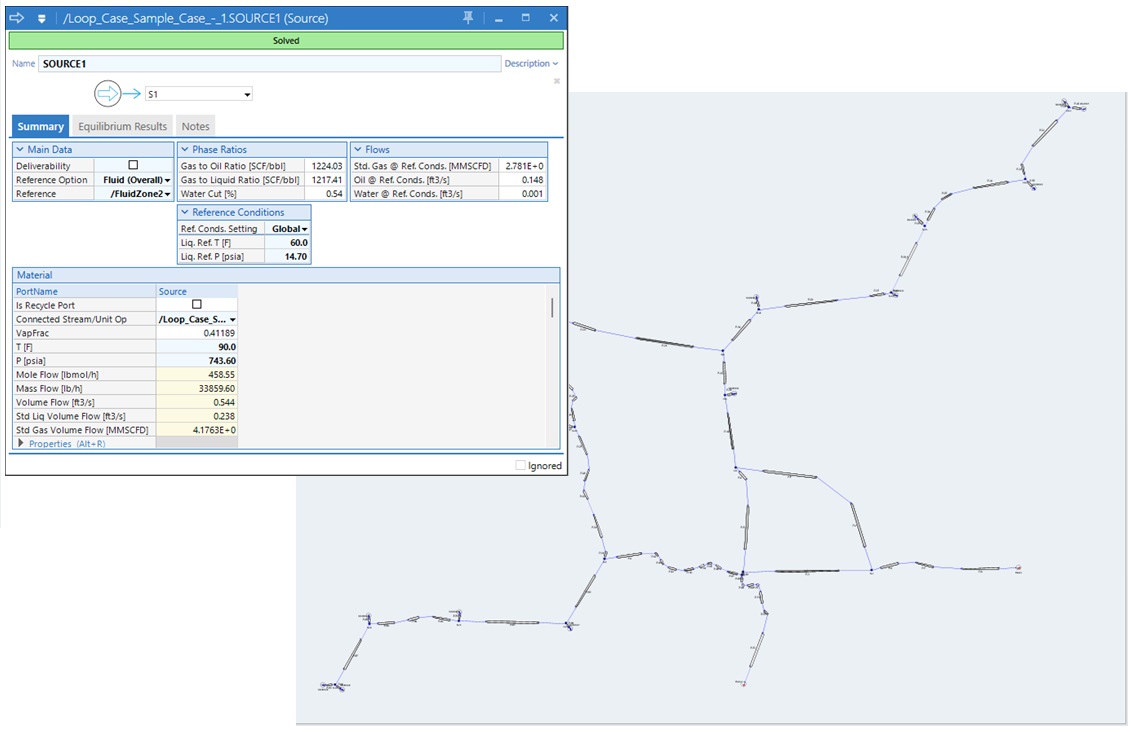
Solve a pipe network with fixed pressure at sources
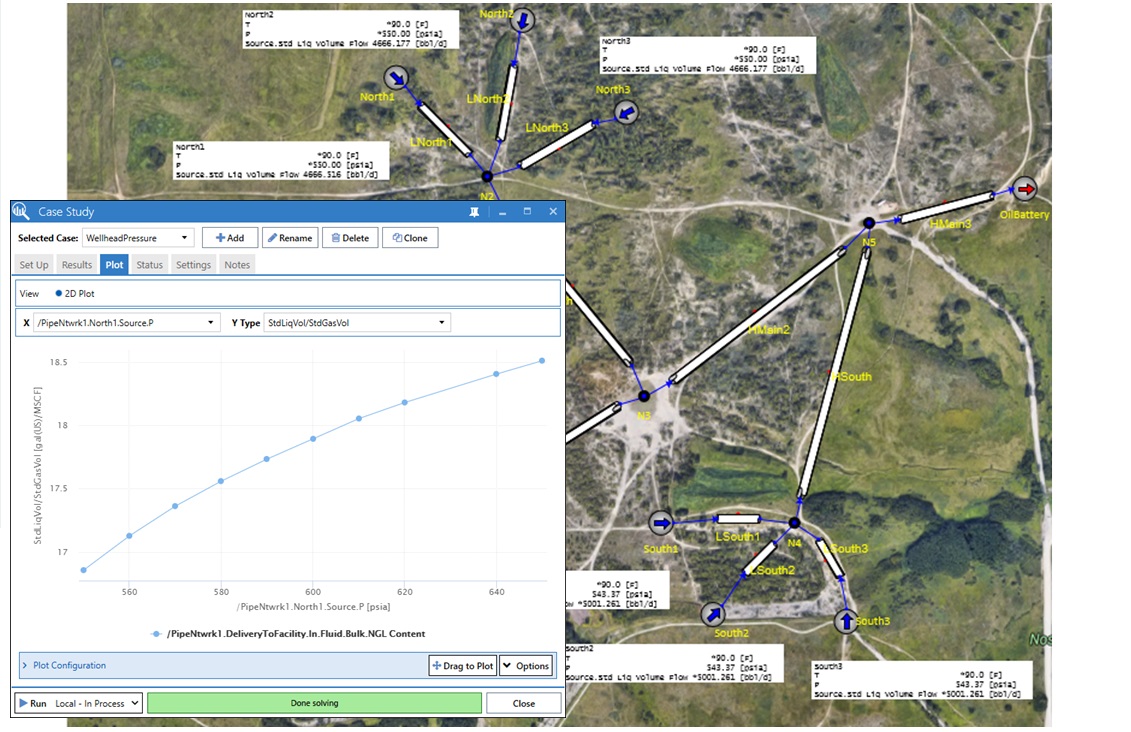
The pipe workspace has been enhanced to enable direct specification of pressure at network sources. Just as in dynamics, steady-state network sources now support pressure specification as an alternative to flow.

In situations where a fixed pressure best represents field metering and control, this specification eliminates the need for controllers to be added to the network, significantly improving usability, solver speed and robustness. Pressure may be specified at all, or a subset of, sources.
Release details
Symmetry™ process simulation software helps users model process workflows in a single collaborative environment, while integrating pipelines, pipe networks, facilities models, and flare systems to enable consistent thermodynamics and fluid characterization across the whole system. With Symmetry software, users can switch between steady-state and dynamic modeling, optimize processes in upstream, midstream, downstream, and new energy sectors, and maximize the total value of the asset.
Symmetry 2024.2 features a next-generation thermodynamics package for carbon capture and gas sweetening applications, the ability to easily conduct green hydrogen production studies over time, and enhanced flexibility and robustness in pipe network modelling.
Predict CO2 capture performance of any solvent
Amines 2 is a new and improved thermodynamic model tailored for CO2 capture and natural gas sweetening, with equilibrium prediction for any solvent makeup, whether chemical (reactive amines), physical (polar), or a combination. Beyond extended validation ranges for incorporated solvents, improvements include enhanced accuracy of phase equilibrium, interaction parameters of solvents and acid gases, and heat of reaction prediction. Activity coefficient and heat of absorption parameters are also exposed for user tuning.
For research and development into novelty solvent formulations and additional tuning to experimental data, Amines 2 offers the flexibility to incorporate user-defined amines and custom reactions beyond those available in the Symmetry software database. Contact us for more information on these advanced features.
Analyze green hydrogen production over time
A newly added “Time-based analysis” tool enables modeling of processes for long-term planning and evaluations. Such steady-state time-based studies are especially relevant in green hydrogen production, where factors like the power available to an electrolyzer, equipment decay, costs, and pricing fluctuate meaningfully over time. A technoeconomic evaluation or operational planning study can be conducted by first specifying how key input parameters change over time, and then tracking pertinent calculated values through a batch run of the simulation. Large input data sets (for example, a weather forecast) can be imported through a csv file and managed in a data source manager for reuse in multiple studies. Time-tracked results are easily exportable as a csv file for further analysis and custom reporting. These productivity tools can thus ease decision making, on the economic feasibility and optimal operation of a green hydrogen project.
Solve a pipe network with fixed pressure at sources
The pipe workspace has been enhanced to enable direct specification of pressure at network sources. Just as in dynamics, steady-state network sources now support pressure specification as an alternative to flow. In situations where a fixed pressure best represents field metering and control, this specification eliminates the need for controllers to be added to the network, significantly improving usability, solver speed and robustness. Pressure may be specified at all, or a subset of, sources.
